Sliding window is a problem solving technique by which we can find the maximum sum of k consecutive values in an n size array or array type data structure. This method usually uses a one-way for loop.
Suppose we are given an array of size n=9 and we need to extract Here is the maximum value of 4 consecutive numbers.
n = [ 5, 7, 1, 4, 3, 6, 2, 9, 2]
If we want to solve this problem by brute force method. In that case our time complexity can be O(n2) or O(n3). Which is very time consuming.
In this case we can use sliding window technique. which can give us the expected answer in O(n) time.
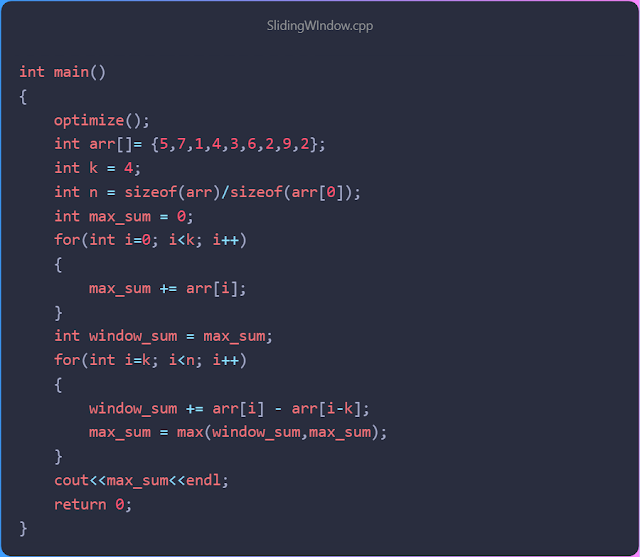
As you can see from the above code, we first extract the sum of the first 4 numbers of the array and put it in max_sum. In the next loop, we add the next numbers and subtract the last number from that sum. Through which we got the sum of every 4 consecutive numbers in the loop.
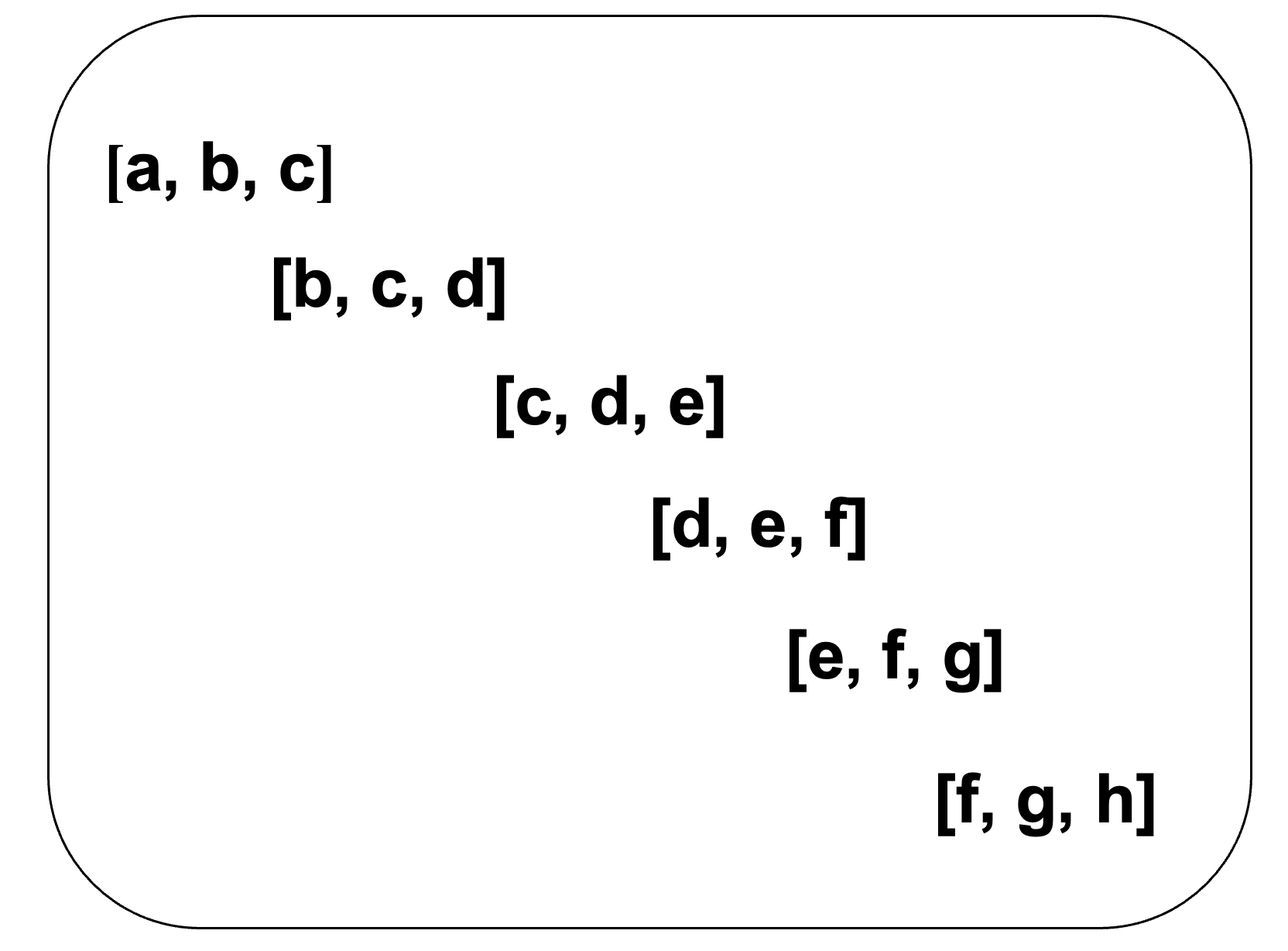
Suppose, the max_sum variable contains the sum of the first four numbers [5, 7, 1, 4]. Now if we add the 5th value of n array to max_sum and subtract the 1st value. So, we can find the sum of values 2-5 of n array. Thus we will find the sum of all the k consecutive number values in the array.
Then by comparing those numbers we find out the highest sum.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Comments
Post a Comment